Karboksilat: Perbedaan antara revisi
Tidak ada ringkasan suntingan Tag: Suntingan perangkat seluler Suntingan aplikasi seluler |
Tidak ada ringkasan suntingan Tag: Suntingan perangkat seluler Suntingan aplikasi seluler |
||
| Baris 5: | Baris 5: | ||
''Garam karboksilat'' memiliki rumus umum M(RCOO)<sub>''n''</sub>, dengan M adalah logam dan ''n'' adalah 1, 2,...; ''ester karboksilat'' memiliki rumus umum RCOOR′. R dan R′ adalah gugus organik; R′ ≠ H. |
''Garam karboksilat'' memiliki rumus umum M(RCOO)<sub>''n''</sub>, dengan M adalah logam dan ''n'' adalah 1, 2,...; ''ester karboksilat'' memiliki rumus umum RCOOR′. R dan R′ adalah gugus organik; R′ ≠ H. |
||
Suatu '''ion karboksilat''' adalah [[basa konjugat]] dari asam karboksilat, RCOO<sup>−</sup>. Ia adalah [[ion]] |
Suatu '''ion karboksilat''' adalah [[basa konjugat]] dari asam karboksilat, RCOO<sup>−</sup>. Ia adalah [[ion]] [[muatan listrik|bermuatan negatif]]. |
||
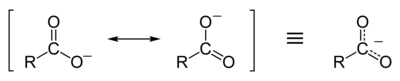
== Resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion== |
== Resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion== |
||
Revisi per 19 Agustus 2017 17.55


Suatu karboksilat adalah suatu garam atau ester dari asam karboksilat. Garam karboksilat memiliki rumus umum M(RCOO)n, dengan M adalah logam dan n adalah 1, 2,...; ester karboksilat memiliki rumus umum RCOOR′. R dan R′ adalah gugus organik; R′ ≠ H.
Suatu ion karboksilat adalah basa konjugat dari asam karboksilat, RCOO−. Ia adalah ion bermuatan negatif.
Resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion
Carboxylic acids easily dissociate into a carboxylate anion and a positively charged hydrogen ion (proton), much more readily than alcohols do (into an alkoxide ion and a proton), because the carboxylate ion is stabilized by resonance. The negative charge that is left after deprotonation of the carboxyl group is delocalized between the two electronegative oxygen atoms in a resonance structure.
This delocalization of the electron cloud means that both of the oxygen atoms are less strongly negatively charged; the positive proton is therefore less strongly attracted back to the carboxylate group once it has left; hence, the carboxylate ion is more stable. In contrast, an alkoxide ion, once formed, would have a strong negative charge on the oxygen atom, which would make it difficult for the proton to escape. Carboxylic acids thus have a lower pH than alcohols: the higher the number of protons in solution, the lower the pH.[1]
Examples
- Formate ion, HCOO−
- Acetate ion, CH3COO−
- Lactate ion, CH3CH(OH)COO−
- Oxalate ion, (COO)2−2
- Citrate ion, C3H5O(COO)3−3
Referensi
- ^ Fox, Marye Anne; Whitesell, James K. (1997). Organic Chemistry (edisi ke-2nd). Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 0-7637-0178-5.